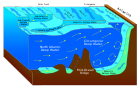
Model Peredaran Am

Model peredaran am (GCM) ialah model matematik bagi peredaran am bagi sesebuah atmosfera atau lautan planet dan berdasarkan persamaan Navier–Stokes]] di atas sebuah sfera berputar dengan dengan istilah termodinamik untuk pelbagai sumber tenaga (sinaran, haba pendam). Persamaan ini ialah dasar untuk program komputer kompleks biasanya digunakan untuk mensimulasi atmosfera atau lautan Bumi. GCM atmosfera dan lautan (AGCM dan OGCM) ialah komponen kekunci bagi model iklim global bersama dengan air batu laut dan komponen permukaan darat. GCM dan model iklim global digunakan secara meluas untuk peramalan cuaca, pemahaman iklim, dan pengunjuran perubahan iklim. Versi-versi yang direka untuk aplikasi iklim skala masa dekad hingga abad pada asalnya dicipta oleh Syukuro Manabe dan Kirk Bryan di Makmal Dinamik Bendalir Geofizikal di Princeton, New Jersey.[1] These computationally intensive numerical models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical, and sometimes biological equations.
Lihat juga
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Projek Antara Perbandingan Model Atmosfera (AMIP)
- Pengukuran Sinaran Atmosfera (ARM)
- CCCma
- Climateprediction.net
- Earth Simulator
- EdGCM
- GFDL CM2.X
- Model Multiskala Alam Sekitar Global
- HadCM3
- Model Peredaran Am Perantaraan
- NCAR
- Pemboleh ubah prognosis
Model iklim di Internet
[sunting | sunting sumber]- National Operational Model Archive and Distribution System Diarkibkan 2016-01-30 di Wayback Machine (NOMADS) is a NOAA Web-services based project providing both real-time and retrospective format independent access to climate and weather model data.
- Dapper/DChart Diarkibkan 2011-12-23 di Wayback Machine – plot and download model data referenced by the Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
- http://www.hadleycentre.gov.uk/research/hadleycentre/models/modeltypes.html Diarkibkan 2008-10-13 di Wayback Machine – Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research – general info on their models
- http://www.ccsm.ucar.edu/ – NCAR/UCAR Community Climate System Model (CCSM)
- http://www.climateprediction.net – do it yourself climate prediction
- http://www.giss.nasa.gov/tools/modelE/ – the primary research GCM developed by NASA/GISS (Goddard Institute for Space Studies)
- http://edgcm.columbia.edu/ – the original NASA/GISS global climate model (GCM) with a user-friendly interface for PCs and Macs
- http://www.cccma.bc.ec.gc.ca/ Diarkibkan 2006-11-24 di Wayback Machine – CCCma model info and interface to retrieve model data
- http://nomads.gfdl.noaa.gov/CM2.X/ – NOAA / Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory CM2 global climate model info and model output data files
- http://www.climate.uvic.ca/ – University of Victoria Global climate model, free for download. Leading researcher was a contributing author to the recent IPCC report on climate change.
Templat:Model Atmosfera, Oseanografi dan Iklim Templat:Pemodelan komputer
Nota
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ ": The First Climate Model". NOAA 200th Celebration. 2007. Dicapai pada 20 April 2010.
Rujukan
[sunting | sunting sumber]- IPCC AR4 SYR (2007), Core Writing Team; Pachauri, R.K; and Reisinger, A. (penyunting), Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report (SYR), Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva, Switzerland: IPCC, ISBN 92-9169-122-4CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link).
Bacaan lanjut
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Ian Roulstone and John Norbury (2013). Invisible in the Storm: the role of mathematics in understanding weather. Princeton University Press.
Pautan luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Climate Change Prediction: A challenging scientific problem (2005). By Prof. A.J. Thorpe. Explains how predictions of future climate change are made using climate models.
- Climate Simulations for 1951–2050 with a Coupled Atmosphere–Ocean Model by Sun and Hansen (2003)
- History of Global Climate Modelling
- E-Media from GFDL's CCVP Group. Includes videos, animations, podcasts and transcripts on climate models.
- [1] GFDL's Flexible Modeling System containing code for the climate models.
- Dapper/DChart Diarkibkan 2011-12-23 di Wayback Machine – plot and download model data referenced by the Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
- Chapter 8: Climate Models and Their Evaluation Diarkibkan 2010-09-22 di Wayback Machine. The IPCC Working Group I Fourth Assessment Report (2007).
- CCSP, 2008: Climate Models: An Assessment of Strengths and Limitations Diarkibkan 2012-08-06 di Wayback Machine A Report by the U.S. Climate Change Science Program and the Subcommittee on Global Change Research [Bader D.C., C. Covey, W.J. Gutowski Jr., I.M. Held, K.E. Kunkel, R.L. Miller, R.T. Tokmakian and M.H. Zhang (Authors)]. Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, Washington, D.C., USA, 124 pp.
- BBC News: Models 'key to climate forecasts'. Dr Vicky Pope of the Hadley Centre explains how computer models are used to predict the day-to-day weather and changes to the climate (2007).
- The scientific basis for projections of climate change (in a nutshell). Video of a lecture given at Princeton University by Isaac Held, Professor of Geosciences and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Princeton University and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL). 26 February 2008.
- (IPCC 2001 section 8.3) – on model hierarchy
- (IPCC 2001 section 8) – much information on coupled GCM's
- Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Diarkibkan 2016-03-07 di Wayback Machine
- On the Radiative and Dynamical Feedbacks over the Equatorial Pacific Cold Tongue
- Basic Radiation Calculations – The Discovery of Global Warming
- Henderson-Sellers, A.; Robinson, P. J. (1999). Contemporary Climatology. New York: Longman. ISBN 0-582-27631-4.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)