Caucasus: Perbezaan antara semakan
Tiada ringkasan suntingan |
terjemah |
||
| Baris 1: | Baris 1: | ||
{{Terjemah}} |
{{Terjemah|en|Caucasus}} |
||
'''Caucasus''' |
'''Caucasus'''atau '''Caucas''' (juga dirujuk sebagai '''Caucasia''',<ref>http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/caucasia Merriam-Webster</ref>{{lang-ady| Къэфкъас}}; {{lang-ru|Кавка́з}}) ialah sebuah wilayah di [[Eropah Timur]] dan [[Asia Barat]] di antara [[Laut Hitam]] dan [[Laut Kaspia]] yang termasuk [[Pergunungan Caucasus]] dan daerah-daerah rendah lainnya. Caucasus kadang-kala dianggap sebagai sebahagian dari [[Asia Tengah]]. Caucasus adalah salah satu daerah yang mempunyai keanekaragaman [[linguistik]] dan [[budaya]] yang paling luas di dunia. |
||
Puncak tertinggi di Caucasus adalah [[Elbrus]] (5.642m), yang juga dianggap sebagai gunung tertinggi di [[Eropah]]. |
Puncak tertinggi di Caucasus adalah [[Gunung Elbrus]] (5.642m), yang juga dianggap sebagai gunung tertinggi di [[Eropah]]. |
||
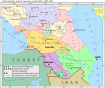
[[Fail:Caucasus countries.png|thumb|200px|Negara-negara Caucasus]] |
|||
[[Negara|Negara-negara]] merdeka yang membentuk Caucasus kini adalah [[Rusia]] (Distrik [[Caucasus Utara]]), [[Georgia]], [[Armenia]] dan [[Azerbaijan]]. Wilayah besar tidak merdeka di Caucasus meliputi [[Ossetia]], [[Chechnya]], [[Ingushetia]] dan [[Dagestan]] di antaranya. Caucasus adalah salah satu daerah yang mempunyai keanekaragaman [[linguistik]] dan [[budaya]] yang paling luas di dunia. |
|||
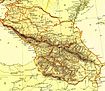
[[Fail:Caucasus region 1994.jpg|thumb|200px|Peta 1994 kawasan Caucasus, menunjukkan lokasi sumber berharga]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Bahagian selatan Caucasus dikenali juga sebagai [[Transcaucasus]]. |
|||
* [[Georgia (negara)|Georgia]] (termasuk [[Abkhazia]] dan [[Ossetia Selatan]] yang dipertikai) |
|||
Kejadian-kejadian bersejarah: |
|||
* Perang [[Bangsa Arab|Arab]]-[[Khazar]] |
|||
* Penjajahan Caucasus oleh [[Rusia]] |
|||
* [[1991]]: Dikenalnya kembali status merdeka negara [[Armenia]], [[Georgia]], dan [[Azerbaijan]] |
|||
Dalam [[mitologi Yunani]], '''Caucasus''' atau '''Caucasos''' adalah salah satu pilar pendokong dunia. [[Prometheus]] dikatakan telah dirantai di sana oleh [[Zeus]]. |
|||
== Lihat pula == |
|||
*[[Orang Ibero-Caucasia]] |
|||
*[[Bahasa Ibero-Caucasia]] |
|||
*[[Jalur Pipa BTC]] |
|||
[[Kategori:Caucasus| ]] |
|||
[[Kategori:Eropah Timur]] |
|||
{{dablink|This article is about the geographic region in Eurasia. For other uses, see [[Caucasus (disambiguation)]] and [[Caucasia (disambiguation)]]}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Georgia (negara)|Georgia]] (including disputed, [[International recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia|partially recognized]] [[Abkhazia]] and [[South Ossetia]]) |
|||
* [[Armenia]] |
* [[Armenia]] |
||
* [[Azerbaijan]] ( |
* [[Azerbaijan]] (termasuk [[Republik Nagorno-Karabakh]]) |
||
* [[Iran]] |
* [[Iran]] |
||
== Etimologi == |
== Etimologi == |
||
| ⚫ | The word Caucasus derives from [[Caucas]], the ancestor of the North Caucasians.<ref>G.Qoranashvili (1995), ''Questions of Ethnic Identity According to Leonti Mroveli's Historical Chronicles'', Studies, Vol. 1, Tbilisi.</ref> He was a son of [[Togarmah]], grandson of Biblical [[Noah]]'s third son [[Japheth]]. According to [[Leonti Mroveli]] after the fall of the [[Tower of Babel]] and the division of humanity into different languages, [[Togarmah]] settled with his sons: [[Kartlos]], [[Haik]] ([[Georgian language|Georgian]]:''ჰაოს'', ''Haos''), [[Movakos]], [[Lekos]] ([[Lak people]]), [[Heros]] ([[Hereti|Kindgom of Hereti]], [[Kavkas]], and [[Egros]] ([[Egrisi|Kingdom of Egrisi]]) between two inaccessible mountains, presumably [[Mount Ararat]] and [[Mount Elbrus]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
== Geografi == |
== Geografi == |
||
The [[Caucasus Mountains]] are generally perceived to be a dividing line between Asia and Europe, and territories in Caucasia are alternately considered to be in one or both [[continent]]s. The highest peak in the Caucasus is [[Mount Elbrus]] (5,642 m) which, in the western Ciscaucasus in Russia, is generally considered the highest point in Europe. |
The [[Caucasus Mountains]] are generally perceived to be a dividing line between Asia and Europe, and territories in Caucasia are alternately considered to be in one or both [[continent]]s. The highest peak in the Caucasus is [[Mount Elbrus]] (5,642 m) which, in the western Ciscaucasus in Russia, is generally considered the highest point in Europe. |
||
| Baris 56: | Baris 32: | ||
The ''Transcaucasus'' is bordered on the north by [[Russia]], on the west by the [[Black Sea]] and [[Turkey]], on the east by the [[Caspian Sea]], and on the south by [[Iran]]. It includes the [[Caucasus Mountains]] and surrounding lowlands. All of Armenia, Azerbaijan (excluding the northern parts) and Georgia (excluding the northern parts) are in South Caucasus. |
The ''Transcaucasus'' is bordered on the north by [[Russia]], on the west by the [[Black Sea]] and [[Turkey]], on the east by the [[Caspian Sea]], and on the south by [[Iran]]. It includes the [[Caucasus Mountains]] and surrounding lowlands. All of Armenia, Azerbaijan (excluding the northern parts) and Georgia (excluding the northern parts) are in South Caucasus. |
||
<!-- |
|||
== Sejarah == |
== Sejarah == |
||
{{see| |
{{see|Sejarah Caucasus}} |
||
Located on the peripheries of [[Turkey]] and [[Russia]], the region has been an arena for political, military, religious, and cultural rivalries and expansionism for centuries. Throughout its history, the Caucasus was usually incorporated into the [[Greater Iran|Iranian world]]. At the beginning of the 19th century, the [[Russian Empire]] conquered the territory from the [[Qajars]].<ref>[http://www.iranica.com/newsite/articles/v5f1/v5f1a032.html Thorez, Pierre. "Caucasus." ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'' - 2 June 2007]</ref> |
Located on the peripheries of [[Turkey]] and [[Russia]], the region has been an arena for political, military, religious, and cultural rivalries and expansionism for centuries. Throughout its history, the Caucasus was usually incorporated into the [[Greater Iran|Iranian world]]. At the beginning of the 19th century, the [[Russian Empire]] conquered the territory from the [[Qajars]].<ref>[http://www.iranica.com/newsite/articles/v5f1/v5f1a032.html Thorez, Pierre. "Caucasus." ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'' - 2 June 2007]</ref> |
||
| Baris 76: | Baris 52: | ||
== Demografi == |
== Demografi == |
||
{{ |
{{utama|Masyarakat Caucasus}} |
||
{{see| |
{{see|Bahasa di Caucasus}} |
||
Setiap wilayah di Caucasus mempunyai perbezaan dalam pertuturan dan bahasanya serta ia juga mempunyai pelbagai keluarga bahasa. Terdapat juga lebih daripada 50 kumpulan etnik yang hidup di setiap wilayah di Caucasus.<ref>[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9021862/Caucasian-peoples Caucasian peoples], ''[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]''</ref> No less than three language families are unique for the area, but also Indo-European languages such [[Armenian language|Armenian]] and [[Ossetic language|Ossetic]], and the Altaic language [[Azerbaijani language|Azerbeijani]] are local to the area. |
Setiap wilayah di Caucasus mempunyai perbezaan dalam pertuturan dan bahasanya serta ia juga mempunyai pelbagai keluarga bahasa. Terdapat juga lebih daripada 50 kumpulan etnik yang hidup di setiap wilayah di Caucasus.<ref>[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9021862/Caucasian-peoples Caucasian peoples], ''[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]''</ref> No less than three language families are unique for the area, but also Indo-European languages such [[Armenian language|Armenian]] and [[Ossetic language|Ossetic]], and the Altaic language [[Azerbaijani language|Azerbeijani]] are local to the area. |
||
| Baris 87: | Baris 62: | ||
== Dalam mitologi == |
== Dalam mitologi == |
||
In Greek mythology the Caucasus, or Kaukasos, was one of the pillars supporting the world. After presenting man with the gift of fire, [[Prometheus]] was chained there by [[Zeus]], to have his liver eaten daily by an eagle. |
In Greek mythology the Caucasus, or Kaukasos, was one of the pillars supporting the world. After presenting man with the gift of fire, [[Prometheus]] was chained there by [[Zeus]], to have his liver eaten daily by an eagle. |
||
The Roman poet [[Ovid]] placed Caucasus in [[Scythia]] and depicted it as a cold and stony mountain which was the abode of personified hunger. The Greek hero Jason sailed to the west coast of the Caucasus in pursuit of the [[Golden Fleece]], and there met the famed [[Medea]]. |
The Roman poet [[Ovid]] placed Caucasus in [[Scythia]] and depicted it as a cold and stony mountain which was the abode of personified hunger. The Greek hero Jason sailed to the west coast of the Caucasus in pursuit of the [[Golden Fleece]], and there met the famed [[Medea]]. |
||
--> |
|||
== Sumber asli (tenaga dan mineral) == |
== Sumber asli (tenaga dan mineral) == |
||
Caucasus mempunyai kepentingan ekonomi terhadap [[mineral]] dan sumber [[tenaga]], seperti: [[alunite]], [[emas]], [[chromium]], [[kuprum]], [[timah besi]], [[raksa (elemen)|raksa]], [[mangan]], [[molybdenum]], [[plumbum]], [[tungsten]], [[uranium]], [[zink]], [[petroleum]], [[gas asli]], and [[arang batu]] (kedua-dua [[arang batu keras|keras]] dan [[arang batu perang|perang]]). |
Caucasus mempunyai kepentingan ekonomi terhadap [[mineral]] dan sumber [[tenaga]], seperti: [[alunite]], [[emas]], [[chromium]], [[kuprum]], [[timah besi]], [[raksa (elemen)|raksa]], [[mangan]], [[molybdenum]], [[plumbum]], [[tungsten]], [[uranium]], [[zink]], [[petroleum]], [[gas asli]], and [[arang batu]] (kedua-dua [[arang batu keras|keras]] dan [[arang batu perang|perang]]). |
||
== Lihat juga == |
== Lihat juga == |
||
*[[Masyarakat Caucasus]] |
*[[Masyarakat Caucasus]] |
||
*[[Sejarah Caucasus]] |
*[[Sejarah Caucasus]] |
||
*[[Negara rentas benua]] |
|||
*[[Transcontinental nation]]s |
|||
*[[Caucasus Selatan]] |
*[[Caucasus Selatan]]/[[Caucasus Utara|Utara]] |
||
*[[Bahasa Caucasus]] |
*[[Bahasa di Caucasus]] |
||
*[[Islam di Russia]] |
*[[Islam di Russia]] |
||
*[[ |
*[[Kebudayaan Georgia]] |
||
*[[ |
*[[Kebudayaan Armenia]] |
||
*[[ |
*[[Kebudayaan Azerbaijan]] |
||
*[[Perang |
*[[Perang Rusia–Circasia]] |
||
*[[Prometheism]] |
*[[Prometheism]] |
||
*[[Pergunungan Ural]] |
|||
== |
== Rujukan == |
||
<div class="references-small"> |
<div class="references-small"> |
||
*Caucasus: A Journey to the Land Between Christianity and Islam By Nicholas Griffin |
*Caucasus: A Journey to the Land Between Christianity and Islam By Nicholas Griffin |
||
*Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus By Svante E. Cornell |
*Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus By Svante E. Cornell |
||
*The Caucasus By Ivan Golovin |
*The Caucasus By Ivan Golovin |
||
* |
|||
* |
* |
||
</div> |
</div> |
||
| Baris 133: | Baris 105: | ||
[[Kategori:Caucasus| ]] |
[[Kategori:Caucasus| ]] |
||
[[Kategori: |
[[Kategori:Kawasan khas biodiversiti]] |
||
[[ar:القوقاز]] |
[[ar:القوقاز]] |
||
Semakan pada 15:30, 27 Ogos 2009
Tolong bantu menterjemahkan sebahagian rencana ini. Rencana ini memerlukan kemaskini dalam Bahasa Melayu piawai Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka. Sila membantu, bahan-bahan boleh didapati di Caucasus (Inggeris). Jika anda ingin menilai rencana ini, anda mungkin mahu menyemak di terjemahan Google. Walau bagaimanapun, jangan menambah terjemahan automatik kepada rencana, kerana ini biasanya mempunyai kualiti yang sangat teruk. Sumber-sumber bantuan: Pusat Rujukan Persuratan Melayu. |
Caucasusatau Caucas (juga dirujuk sebagai Caucasia,[1]Templat:Lang-ady; Rusia: Кавка́з) ialah sebuah wilayah di Eropah Timur dan Asia Barat di antara Laut Hitam dan Laut Kaspia yang termasuk Pergunungan Caucasus dan daerah-daerah rendah lainnya. Caucasus kadang-kala dianggap sebagai sebahagian dari Asia Tengah. Caucasus adalah salah satu daerah yang mempunyai keanekaragaman linguistik dan budaya yang paling luas di dunia.
Puncak tertinggi di Caucasus adalah Gunung Elbrus (5.642m), yang juga dianggap sebagai gunung tertinggi di Eropah.
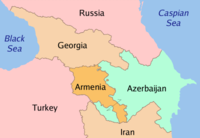

Caucasus Utara (juga digelar Ciscaucasia) terdiri dari:
- Russia (Chechnya, Ingushetia, Dagestan, Adyghea, Kabardino-Balkaria, Karachai-Cherkessia, Ossetia Utara, Krasnodar Krai, Stavropol Krai)
Caucasus Selatan (juga digelar Transcaucasia) terdiri dari:
- Georgia (termasuk Abkhazia dan Ossetia Selatan yang dipertikai)
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan (termasuk Republik Nagorno-Karabakh)
- Iran
Etimologi
The word Caucasus derives from Caucas, the ancestor of the North Caucasians.[2] He was a son of Togarmah, grandson of Biblical Noah's third son Japheth. According to Leonti Mroveli after the fall of the Tower of Babel and the division of humanity into different languages, Togarmah settled with his sons: Kartlos, Haik (Georgian:ჰაოს, Haos), Movakos, Lekos (Lak people), Heros (Kindgom of Hereti, Kavkas, and Egros (Kingdom of Egrisi) between two inaccessible mountains, presumably Mount Ararat and Mount Elbrus.
Geografi
The Caucasus Mountains are generally perceived to be a dividing line between Asia and Europe, and territories in Caucasia are alternately considered to be in one or both continents. The highest peak in the Caucasus is Mount Elbrus (5,642 m) which, in the western Ciscaucasus in Russia, is generally considered the highest point in Europe.
The Caucasus is one of the most linguistically and culturally diverse regions on Earth. The nation-states that comprise the Caucasus today are the post-Soviet states Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Russian divisions include Krasnodar Krai, Stavropol Krai, and the autonomous republics of Adygea, Karachay-Cherkessia, Kabardino-Balkaria, North Ossetia, Ingushetia, Chechnya, and Dagestan. Three territories in the region claim independence but are not acknowledged as nation-states by the international community: Abkhazia, Nagorno-Karabakh and South Ossetia.
The Caucasus is an area of great ecological importance. It harbors some 6,400 species of higher plants, 1,600 of which are endemic to the region.[3] Its native animals include leopards, brown bears, wolves, European bisons, marals and golden eagles. Among invertebrates, some 1,000 spider species are recorded in the Caucasus[4]. The natural landscape is one of mixed forest, with substantial areas of rocky ground above the treeline. The Caucasus Mountains are also famous for a dog breed, the Caucasian Shepherd Dog (Ovcharka).
The northern portion of the Caucasus is known as the Ciscaucasus and the southern portion as the Transcaucasus.
The Ciscaucasus contains the larger majority of the Greater Caucasus Mountain range, also known as the Major Caucasus mountains. It includes Southwestern Russia and northern parts of Georgia and Azerbaijan.
The Transcaucasus is bordered on the north by Russia, on the west by the Black Sea and Turkey, on the east by the Caspian Sea, and on the south by Iran. It includes the Caucasus Mountains and surrounding lowlands. All of Armenia, Azerbaijan (excluding the northern parts) and Georgia (excluding the northern parts) are in South Caucasus.
Sumber asli (tenaga dan mineral)
Caucasus mempunyai kepentingan ekonomi terhadap mineral dan sumber tenaga, seperti: alunite, emas, chromium, kuprum, timah besi, raksa, mangan, molybdenum, plumbum, tungsten, uranium, zink, petroleum, gas asli, and arang batu (kedua-dua keras dan perang).
Lihat juga
- Masyarakat Caucasus
- Sejarah Caucasus
- Negara rentas benua
- Caucasus Selatan/Utara
- Bahasa di Caucasus
- Islam di Russia
- Kebudayaan Georgia
- Kebudayaan Armenia
- Kebudayaan Azerbaijan
- Perang Rusia–Circasia
- Prometheism
- Pergunungan Ural
Rujukan
- Caucasus: A Journey to the Land Between Christianity and Islam By Nicholas Griffin
- Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus By Svante E. Cornell
- The Caucasus By Ivan Golovin
- ^ http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/caucasia Merriam-Webster
- ^ G.Qoranashvili (1995), Questions of Ethnic Identity According to Leonti Mroveli's Historical Chronicles, Studies, Vol. 1, Tbilisi.
- ^ Endemic Species of the Caucasus
- ^ Caucasian Spiders » CHECKLISTS & MAPS
Pautan luar
- Ethnographic map of Caucasus
- (Caucasian Review of International Affairs - an academic journal on the South Caucasus)
- BBC News: North Caucasus at a glance, 8 September 2005
- United Nations Environment Programme map: Landcover of the Caucasus
- United Nations Environment Programme map: Population density of the Caucasus
- Caucasus and Iran entry in Encyclopaedia Iranica
- University of Turin-Observatory on Caucasus